38 identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.
study.com › learn › cell-division-questions-andCell Division Questions and Answers | Study.com A cell entering the cell cycle with 32 chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each with _____. A) 16 chromosomes B) 32 chromosomes C) 32 pairs of chromosomes D) 64 pairs of chromosomes ... Interactive Eukaryotic Cell Model - CELLS alive Nucleus: The nucleus is the most obvious organelle in any eukaryotic cell. It is enclosed in a double membrane and communicates with the surrounding cytosol via numerous nuclear pores. Within each nucleus is nuclear chromatin that contains the organism’s genome. The chromatin is efficiently packaged within the small nuclear space.
› cells › 3dcellInteractive Cell Models - CELLS alive Living cells are divided into two types - prokaryotic and eukaryotic (sometimes spelled procaryotic and eucaryotic). This division is based on internal complexity. The following interactive animations provide graphic roadmaps to the organization of both of these cell types.
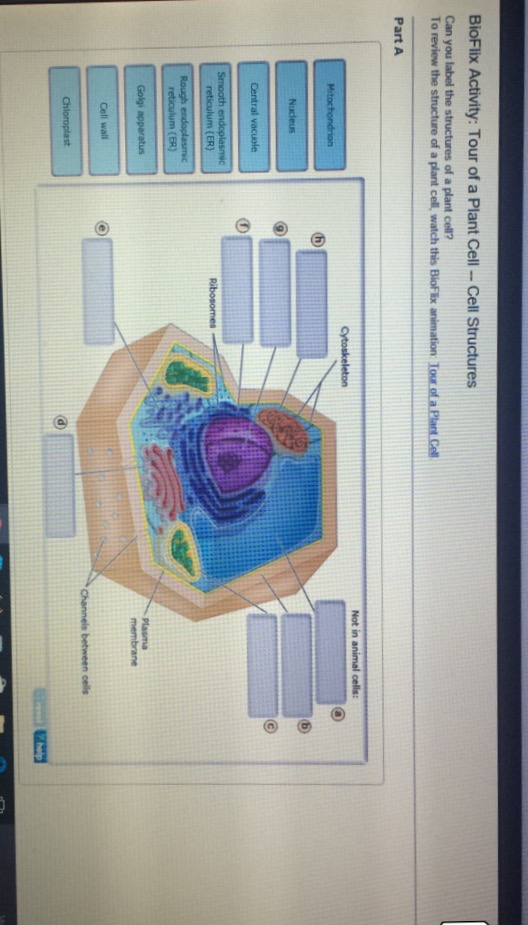
Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.
› books › NBK21120Genome Anatomies - Genomes - NCBI Bookshelf When you have read Chapter 2, you should be able to: Draw diagrams illustrating the major differences between the genetic organizations of the genomes of humans, plants, insects, yeast and bacteria, and give an explanation for the C-value paradoxDescribe the DNA-protein interactions that give rise to the chromatosome and the 30 nm chromatin fiberState the functions of centromeres and telomeres ... Introduction to Cells: The Grand Cell Tour - YouTube Compares and contrasts prokaryote cells and eukaryote cells before exploring organelle structures and functions! Video includes the modern cell theory and p... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Cell_(biology)Cell (biology) - Wikipedia Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body Archived 2020-01-22 at the Wayback Machine in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell Archived 2017-09-27 at the Wayback Machine fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small ...
Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.. The Best AP® Biology Review Guide for 2022 | Albert Resources Mar 01, 2022 · ENE-2.K: Describe the membrane- bound structures of the eukaryotic cell. ... Part B: identify experimental design procedures (3-4 pts.) Part C: analyze data (1-3 pts.) ... fully addressing each part. Additionally, within the AP® Biology … Cell (biology) - Wikipedia Prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea, two of the three domains of life.Prokaryotic cells were the first form of life on Earth, characterized by having vital biological processes including cell signaling.They are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells, and lack a nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The DNA of a prokaryotic cell consists of a single circular … › cells › cell_modelInteractive Eukaryotic Cell Model - CELLS alive Nucleus: The nucleus is the most obvious organelle in any eukaryotic cell. It is enclosed in a double membrane and communicates with the surrounding cytosol via numerous nuclear pores. Within each nucleus is nuclear chromatin that contains the organism’s genome. The chromatin is efficiently packaged within the small nuclear space. Cell Biology Questions and Answers - Study.com The ICF of a red blood cell is approximately 0.3 OsM (osmolar). Explain what will happen to a red blood cell that is placed in 0.3 M Urea. Indicate the osmolarity of each solution (i.e. hyposmotic,...
The proteogenomic subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia - Cell Mar 03, 2022 · Jayavelu et al. perform an integrated multi-omics approach to elucidate the proteogenomic landscape of acute myeloid leukemia. Five proteomic AML subtypes are identified, each reflecting specific biological features. One proteomic subtype (Mito-AML) is characterized by high expression of mitochondrial proteins, shows poor outcome, and is hyper-dependent on … › pmc › articlesSingle‐cell RNA sequencing technologies and applications: A ... Mar 29, 2022 · 1. THE RISE OF SINGLE‐CELL RNA SEQUENCING TECHNOLOGY. Humans are highly organized systems composed of approximately 3.72 × 10 13 cells of various types forming harmonious microenvironments to keep proper organ functions and normal cellular homeostasis. 1 Living cells were observed for the very first time in the 16th century, and since then many signs of progress and advancement of new ... › watchIntroduction to Cells: The Grand Cell Tour - YouTube Compares and contrasts prokaryote cells and eukaryote cells before exploring organelle structures and functions! Video includes the modern cell theory and p... Genome Anatomies - Genomes - NCBI Bookshelf When you have read Chapter 2, you should be able to: Draw diagrams illustrating the major differences between the genetic organizations of the genomes of humans, plants, insects, yeast and bacteria, and give an explanation for the C-value paradoxDescribe the DNA-protein interactions that give rise to the chromatosome and the 30 nm chromatin fiberState the …
Interactive Cell Models - CELLS alive Eukaryotic Cell Organelles. Prokaryotic Cell Model. Unique Animal, Plant and Bacteria Characteristics. For life all cells have basic needs. Cells have diverged in their structure and function to accommodate these survival requirements. Here are some KEY TERMS to help you think, explore and search for similarities and significant differences ... Single‐cell RNA sequencing technologies and applications: A brief ... Mar 29, 2022 · 1. THE RISE OF SINGLE‐CELL RNA SEQUENCING TECHNOLOGY. Humans are highly organized systems composed of approximately 3.72 × 10 13 cells of various types forming harmonious microenvironments to keep proper organ functions and normal cellular homeostasis. 1 Living cells were observed for the very first time in the 16th century, and since … Cell Division Questions and Answers | Study.com A cell entering the cell cycle with 32 chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each with _____. A) 16 chromosomes B) 32 chromosomes C) 32 pairs of chromosomes D) 64 pairs of chromosomes ... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Cell_(biology)Cell (biology) - Wikipedia Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body Archived 2020-01-22 at the Wayback Machine in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell Archived 2017-09-27 at the Wayback Machine fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small ...
Introduction to Cells: The Grand Cell Tour - YouTube Compares and contrasts prokaryote cells and eukaryote cells before exploring organelle structures and functions! Video includes the modern cell theory and p...
› books › NBK21120Genome Anatomies - Genomes - NCBI Bookshelf When you have read Chapter 2, you should be able to: Draw diagrams illustrating the major differences between the genetic organizations of the genomes of humans, plants, insects, yeast and bacteria, and give an explanation for the C-value paradoxDescribe the DNA-protein interactions that give rise to the chromatosome and the 30 nm chromatin fiberState the functions of centromeres and telomeres ...


Post a Comment for "38 identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell."