43 atp molecule label
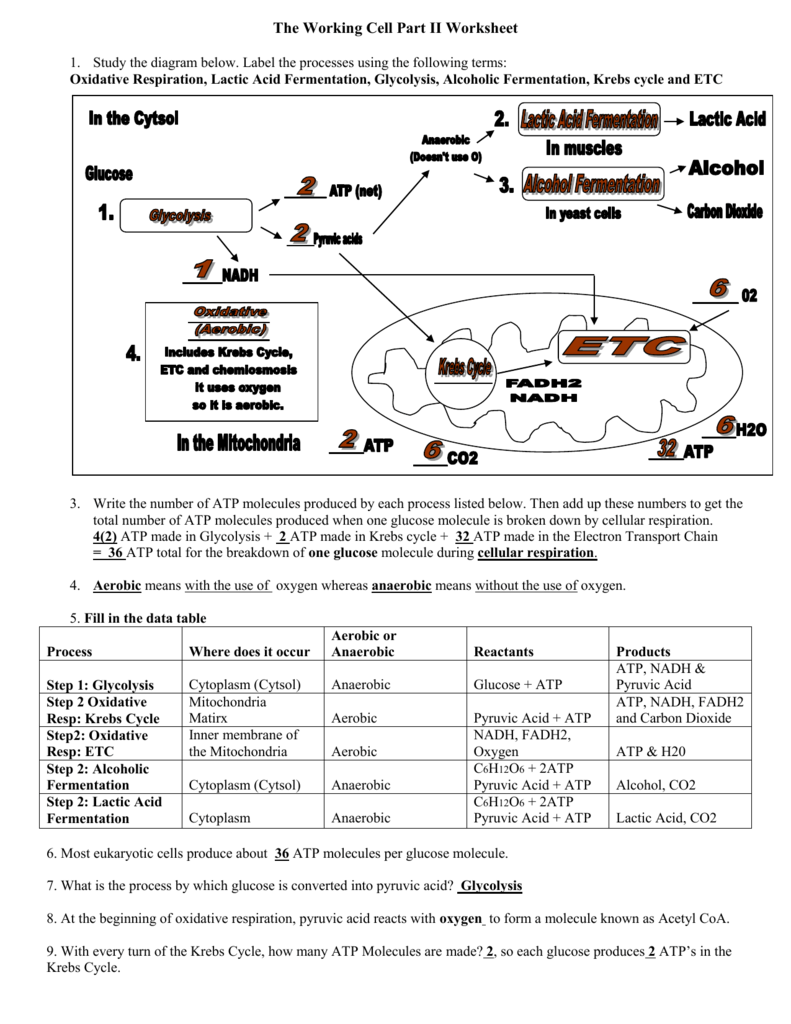
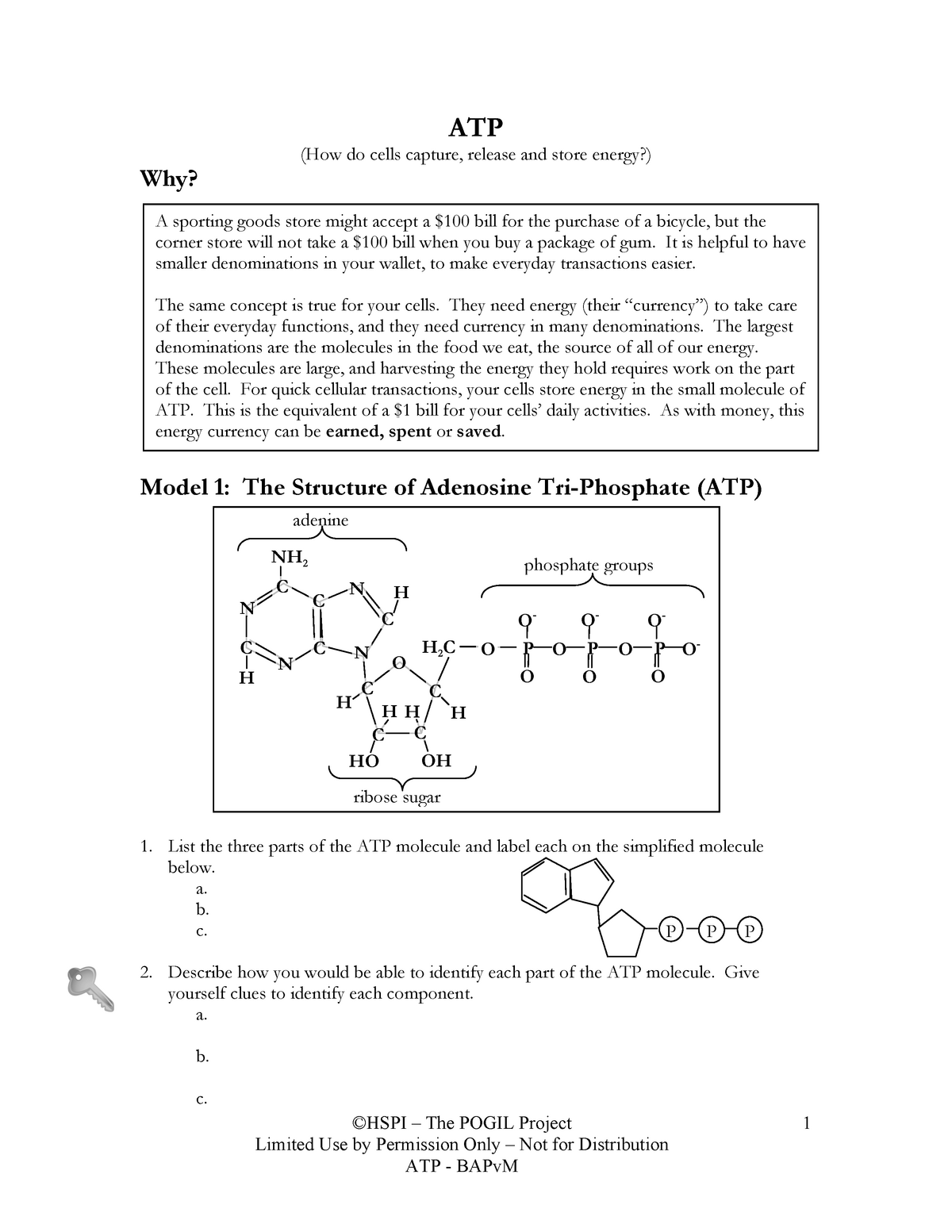
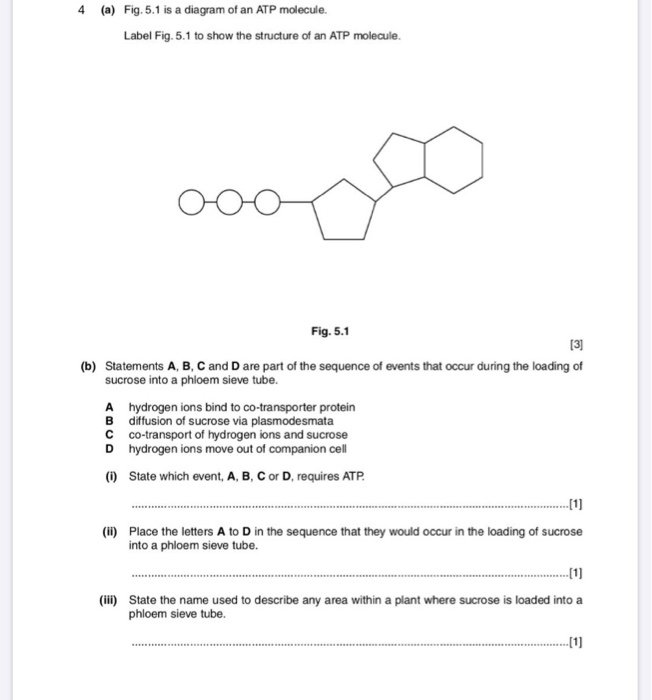
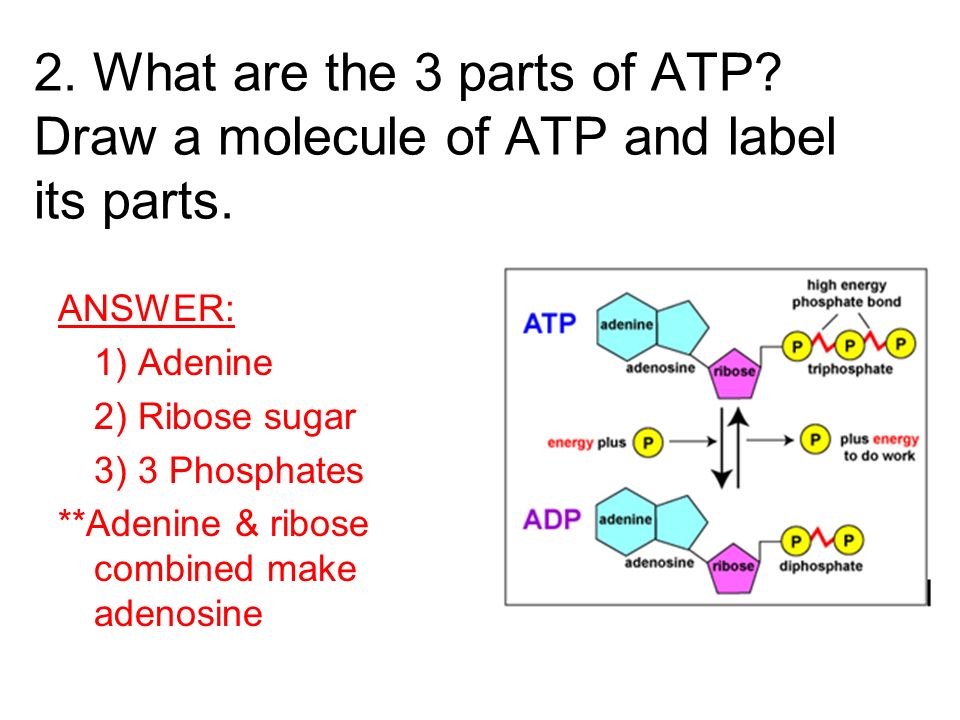
1 draw and label an atp molecule make sure to include 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Make sure to include the 3 parts. 2. What is the process called when a phosphate is added to the ADP molecule a. Photosynthesis b. Phosphorylation c. Permeability d. Precipitation 3. The metabolism (breakdown) of ________________ in the mitochondria provides the energy for the phosphorylation ofADP.a. ATP b. PDF worksheet chemical energy and ATP - Frontier Central School District Identify the parts of an ATP molecule below: (Label adenosine, ribose, ... What happens to the ATP molecule when a phosphate group is removed ? (what does it turn into?) 8. Draw a diagram below showing the cycle of ATP and ADP below (see Figure 4.2 on page 101) 9. What type of organic compounds store the most energy?
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate | C10H16N5O13P3 - PubChem Adenosine-5'-triphosphate | C10H16N5O13P3 | CID 5957 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological ...
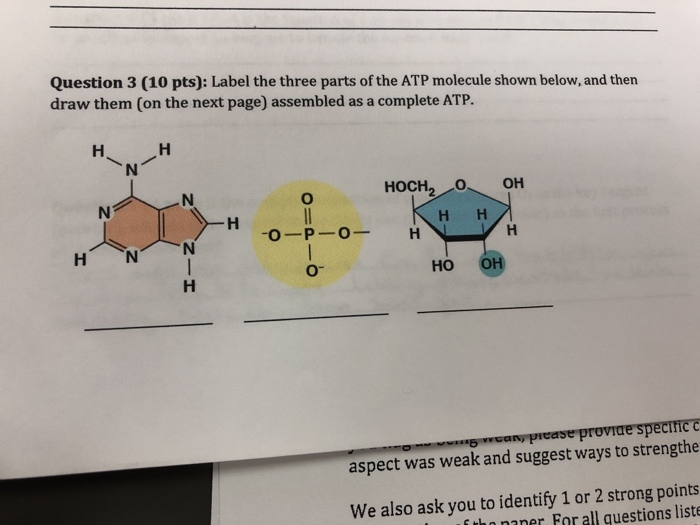
Atp molecule label
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive Description This model shows the structure of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. ATP has many important roles in the cell. A major role of ATP is to bind to and activate enzymes called kinases. Structural and mechanistic analysis of a tripartite ATP ... Aug 04, 2022 · Tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transporters are found widely in bacteria and archaea and consist of three structural domains, a soluble substrate-binding protein (P-domain), and two ... The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. For 3-D Structure of this image using Jsmol Click here
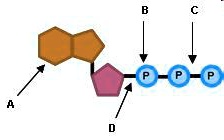
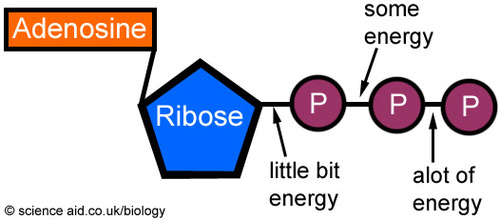
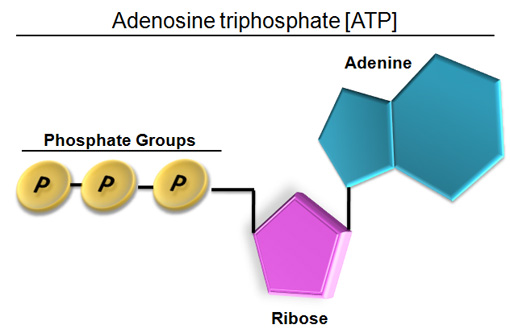
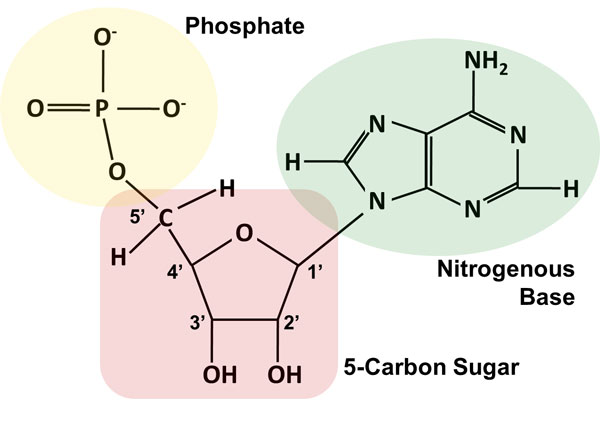
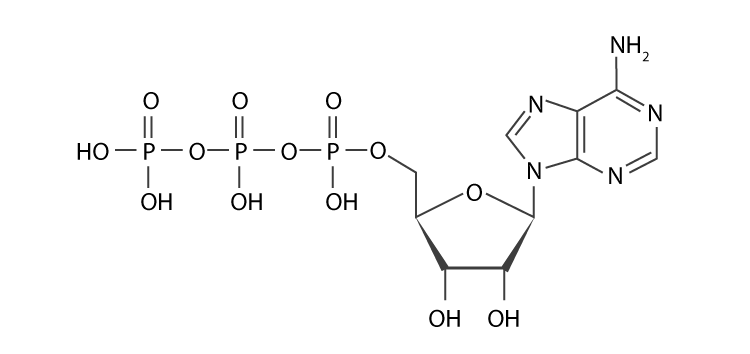
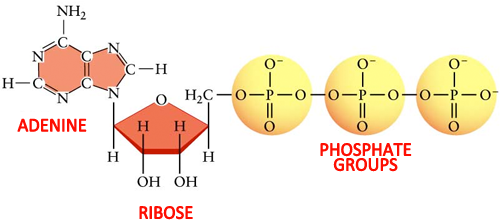
Atp molecule label. ATP reading and coloring activity.pdf - Read, Answer, Color, Label ... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by cells to do work. It is a nucleotide consisting of a nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine), a 5-carbon sugar, and 3 phosphate groups. ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. The last two phosphate groups are joined by high energy bonds. How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com ATP is made up of adenine, ribose, and three phosphate molecules. ATP contains one adenine (blue), one sugar (pink), and three phosphate groups. ATP Meaning ATP follows the same rules of... ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate | OpenStax Biology 2e - Lumen Learning ATP is the primary energy-supplying molecule for living cells. ATP is comprised of a nucleotide, a five-carbon sugar, and three phosphate groups. The bonds that connect the phosphates (phosphoanhydride bonds) have high-energy content. The energy released from ATP hydrolysis into ADP + P i performs cellular work. ATP | ≥99%(HPLC) | Selleck | Immunology & Inflammation related chemical ATP. Catalog No.S5260 Synonyms: Adenosine-Triphosphate, Adenosine 5'-triphosphate. For research use only. ATP (Adenosine-Triphosphate, Adenosine 5'-triphosphate) is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate and an important endogenous signaling molecule in immunity and inflammation. CAS No. 56-65-5.
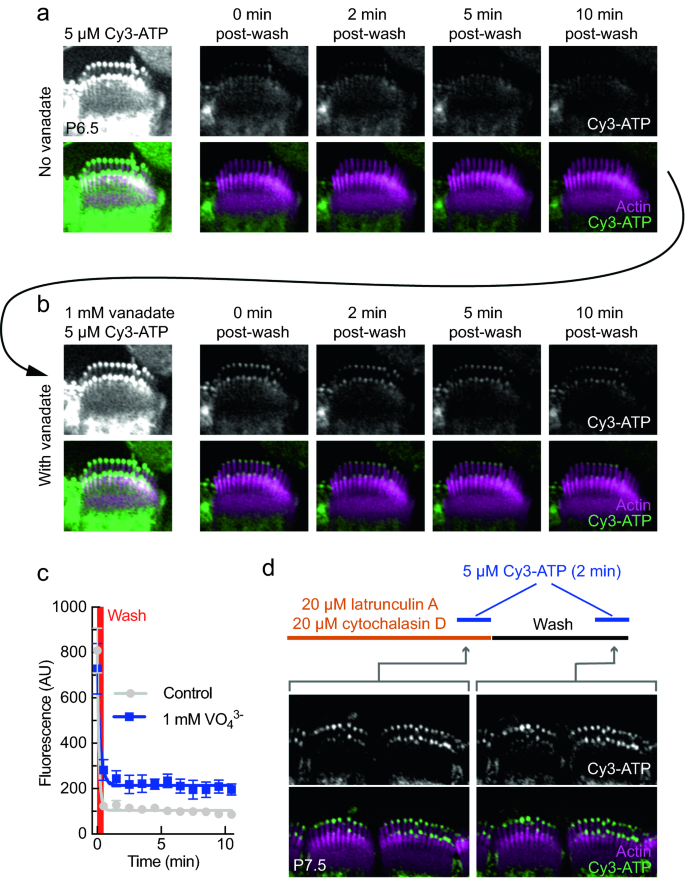
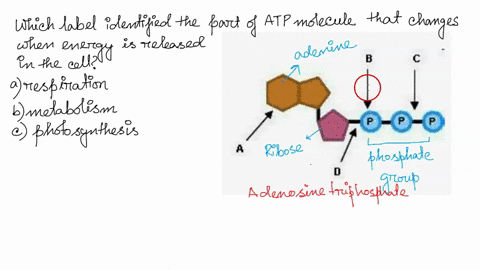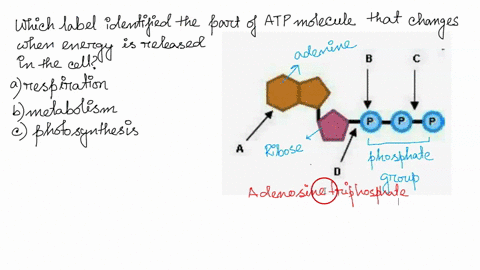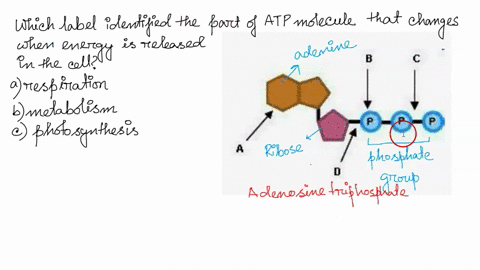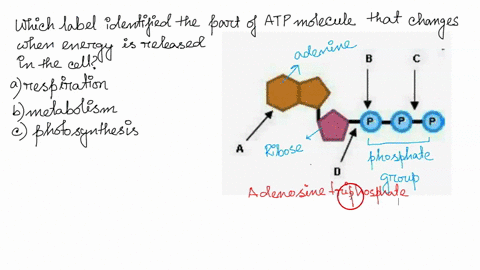
RCSB PDB - ATP Ligand Summary Page nutraceutical. Description. An adenine nucleotide containing three phosphate groups esterified to the sugar moiety. In addition to its crucial roles in metabolism adenosine triphosphate is a neurotransmitter. Synonyms. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate. Adenosine triphosphate disodium trihydrate. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate. ATP Flashcards | Quizlet Germinating peas at 20ºC have a higher rate of cellular respiration than germinating peas at 10ºC. Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when energy is released in the cells of all living things, and what is the name of this process? C; respiration ATP is produced during the process of cellular respiration. 1Q1K: Structure Of Atp-phosphoribosyltransferase From E. Coli Complexed ... ATP PHOSPHORIBOSYLTRANSFERASEL(+)-Tartaric AcidPhosphoribosyl Atp. NCBI. National Center for Biotechnology Information. ... Label Count Molecule; Proteins (6 molecules) A. A_1. A_2. A_3. A_4. A_5. 6: ATP Phosphoribosyltransferase (Gene symbol: hisG) Chemicals and Non-standard biopolymers (18 molecules) 1. 6. atp molecule Flashcards and Study Sets | Quizlet Biological molecules, Enzyme, DNA, ATP. Polymerase. Monomers. Describe how glucose join form maltose. A large complex molecules composed by a long chain of monomers…. Are small repeat basic molecular unit, which form large molecu…. 1. two glucose combine remove water molecule,... 2. From between….
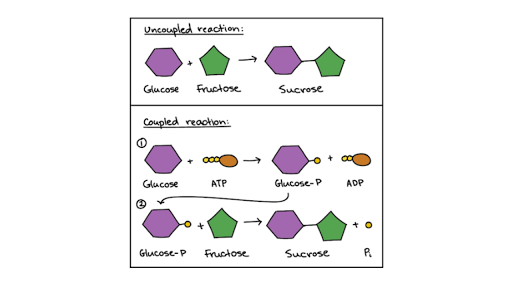
ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy ATP structure, ATP hydrolysis to ADP, and reaction coupling. ATP structure, ATP hydrolysis to ADP, and reaction coupling. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The discovery of ATP was made by Karl Lohman (1929). ATP is a nucleotide consisting of a base-adenine, a pentose sugar-ribose and three phosphate groups. Out of three phosphate groups the last two are attached by high energy rich bonds (Figure 14.3). On hydrolysis, it releases energy (7.3 K cal or 30.6 KJ/ATP) and it is found in all living ... The GTP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules GTP Molecule. GTP (also known as guanylyl imidodiphosphate, guanosine-5'-triphosphate, or guanosine triphosphate) is a chemical compound (nucleotide) that is incorporated into the growing RNA chain during synthesis of RNA and used as a source of energy during synthesis of proteins. GTP is also essential to signal transduction in living cells ... atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. In the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe the FANCM-family DNA helicase FmI1 directs NCO recombination formation during meiosis. u Based on these helicase motifs, a number of helicase superfamilies have been distinguished. In: Spies, M.
PharmaCircle This website uses cookies to help provide you with the best possible online experience. Please read our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy for information about ...
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP.
Solved 5. Here is a molecule of ATP. Label it. Use an arrow - Chegg Here is a molecule of ATP. Label it. Use an arrow to show which bond is likely to break. (4 points) NH2 3. O HO-P-o-o-o-o-o OH OH OH OH OH 1. 2. a. By what process will that bond break? Previous questionNext question COMPANY About Chegg Chegg For Good College Marketing Corporate Development Investor Relations Jobs Join Our Affiliate Program
Learn About the 3 Main Stages of Cellular Respiration - ThoughtCo May 06, 2019 · ATP is ultimately produced by oxidative phosphorylation—the process by which enzymes in the cell oxidize nutrients. The protein ATP synthase uses the energy produced by the electron transport chain for the phosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule) of ADP to ATP. Most ATP generation occurs during the electron transport chain and ...
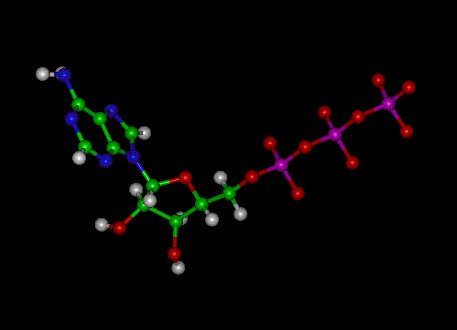
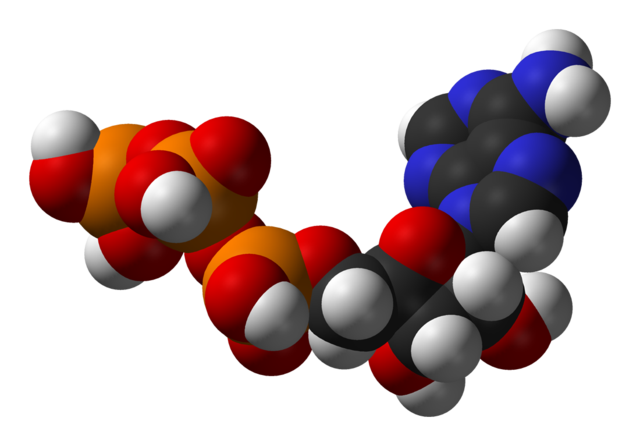
The ATP molecule in 3-D - BioTopics The ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecule has 3 main parts: the base adenine - a double ring like section with several nitrogen atoms (blue), the 5 carbon sugar ribose in the centre, and 3 phosphate groups - a row of phosphorus atoms (orange) surrounded by oxygens (red).
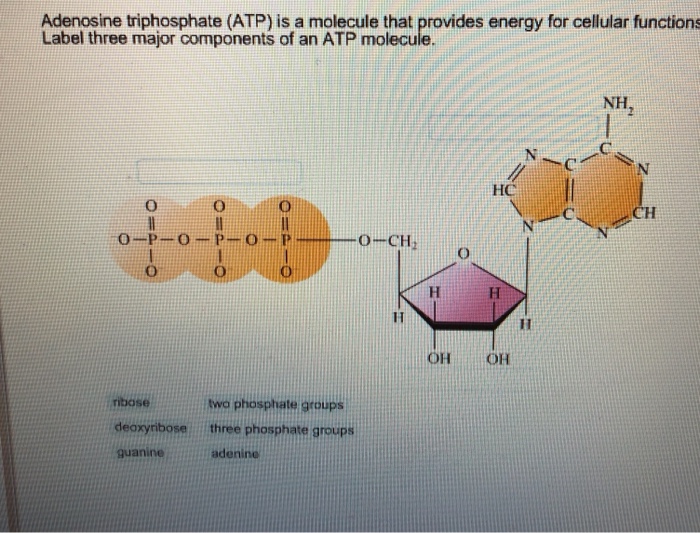
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule | Chegg.com Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions &-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low battery? What arc two ways in which the diagram shows an increase in energy? Describe the concepts shown in the diagram.
Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base ( adenine ), the sugar ribose, and the triphosphate . Contents 1 Structure 1.1 Binding of metal cations to ATP 2 Chemical properties 3 Reactive aspects 4 Production from AMP and ADP
Magnesium in biology - Wikipedia For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP. As such, magnesium plays a role in the stability of all polyphosphate compounds in the cells, including those associated with the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
ATP Molecule Structure: Fuel of Life - Indigo Instruments ATP was first discovered in 1929 by Karl Lohmann. Back then, it was considered that Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) was an energy source produced inside the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. Several years later in 1962, Geoffrey Burnstock discovered that it had the potential to carry messages between cells and that it helps in fighting human diseases.
Ribose - Wikipedia Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C 5 H 10 O 5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH) 4 −H. The naturally-occurring form, d-ribose, is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this compound is necessary for coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes.
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture:
DNA Replication - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Helicases are enzymes that catalyze the unwinding of parental DNA, coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP, ahead of the replication fork. Single-stranded DNA-binding proteins (e.g., eukaryotic replication factor A [RFA]) then stabilize the unwound template DNA, keeping it in an extended single-stranded state so that it can be copied by the polymerase.
Label Atp Molecule - the atp molecule chemical and physical properties ... Label Atp Molecule - 16 images - 35 label each part of the atp molecule labels database 2020, photosynthesis light reactions, energy atp and adp sciencemusicvideos, simple diagram atp molecule diagramaica,
Photosynthesis: Crash Course Biology #8 - YouTube Hank explains the extremely complex series of reactions whereby plants feed themselves on sunlight, carbon dioxide and water, and also create some by product...
Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when ... Answer: C; respiration. Explanation: Cellular respiration is the process by which nutrients such as glucose are broken down using oxygen to generate energy in the form of ATP, that is used to drive cellular processes.; ATP consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phosphate groups in a row. Energy from cellular respiration is stored in the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups ...
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. For 3-D Structure of this image using Jsmol Click here
Structural and mechanistic analysis of a tripartite ATP ... Aug 04, 2022 · Tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transporters are found widely in bacteria and archaea and consist of three structural domains, a soluble substrate-binding protein (P-domain), and two ...
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive Description This model shows the structure of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. ATP has many important roles in the cell. A major role of ATP is to bind to and activate enzymes called kinases.


















Post a Comment for "43 atp molecule label"